In today’s article let me try to make
you understand what is factoring? Explain Different types of factoring?
Introduction to Factoring
The word “Factor” is derived from Latin
word “Facere” which means to make or to do or get things done. Factoring first
came into existence in the year 1920.In initial period factoring is neither
regarded as organized sector nor Association of British Factors. Today the
factoring business is spread out in 60 countries covering more than 100,000 businesses
with a factoring volume of USD 700 billion in a year. 90% of the factoring
turnover comes from USA and European countries. In 1988 RBI appointed a
committee called C.S. Kalyanasundaram Committee which suggested to start
factoring by bank through its subsidiary.
Definition of Factoring
According to Peter M Biscose factoring
can be defined as A continuous relationship between financial institution (a
factor) and a business concern selling goods and/or services (the client) to a
trade customer on an open account basis whereby the factor purchases the
clients book debts (account receivables) with or without recourse to the client
– there by controlling the credit extended to the customer and also
understanding the sales ledgers relevant to the transaction.
Meaning of Factoring
Factoring is an agreement between
seller and a financial institution where by financial institution purchases the
receivables of the customer and also controls and administers the receivables.
In Simple words Factoring agency takes the risk of collecting the receivables
from the respective parties and bears the risk of non-payment of debt and
losses. The specialized activity of factoring firm is to convert the
receivables into Cash.
Factoring is a financial service
covering die financing and collection of receivables both in domestic and
international market.
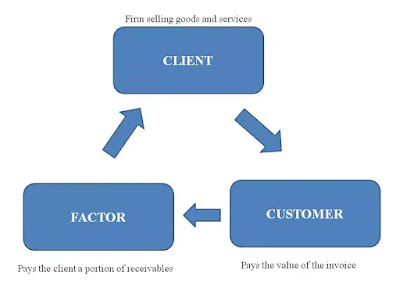
Parties Involves in Factoring
There are three parties involved in factoring. They are
§ Seller(Client)
§ Customer and
§ Factor
Seller
Client
is the person or firm who wants to sell goods or services to customers.
Customer
Customer is the person or firm who
wants to buy the goods and services of client but doesn’t have sufficient funds
to buy them so purchases them on credit.
Factor
Factor is a financial institution
which enters into agreement with client to provide factoring services. The
factor receives the payment from the customer on due date and deducts the
agreed amount and makes the payment to client.
Types of Factoring
Various types of factoring services are as follows,
§ Recourse and Non-Recourse Factoring
In recourse
factoring the receivables purchased if turns out to be bad, then the risk is
completely beared by the client and the factoring agency doesn’t assumes the
credit risk associated with it.
While in
non-recourse factoring the factor bears the complete risk or loss occurred on
the non-payment of the customer and the factor cannot claim the amount from
selling firm or organization.
§ Advance and Maturity Factoring
In advance
factoring the factoring agency pays a fixed percentage amount of the
receivables (usually up to 75%-90%) and up to guaranteed payment of the amount
from customer the rest of the balance amount will paid to the client.
In maturity
factoring no advance is paid to client only on the collection of receivables an
agreed amount is paid to the client. Maturity factoring consists of sale of
account receivables to factor which doesn’t make any advances at the time of
sale.
§ Conventional or Full Factoring
This factoring
is also known as Old Line Factoring. In this factoring the factoring agency
performs almost all the services of the factoring such as collection of
receivables, maintenance of sales ledger, credit control and credit insurance.
The factoring agency sets a limit based on bills outstanding maturity wise and
takes up the corresponding risk of default or credit risk and the factor will
claim the debtor as also the client credit.
§ Domestic and Export Factoring
In domestic
factoring three parties involved resides in the same country. The parties are client,
factor and customer.
In Export Factoring
the parties involved are Exporter (client), importer or customer and export
factor and import factor. This kind of factoring is called Two-factor system of
factoring. In two-factor system results in contract between
·
Exporter(client)
and export factor
·
Export
factor and Import factor
§ Limited Factoring
In Limited
factoring the factoring agency discounts only specific invoices on selective
basis and converts credit bills into cash with respect to selected bills only.
§ Selected Seller based Factoring
Under selected
seller based factoring the seller sells all the account receivables to the
factor along with the delivery challans, contracts etc after invoicing to the
customers. The factoring agency performs all the accounts, collection of debts,
sending reminders and does all the consequential and incidental functions of
the seller. The seller is normally approved by the factor before entering into
the factoring agreement.
§ Selected Buyer based Factoring
Under selected
buyer based factoring the factoring agency first selects buyers based on
creditworthiness and goodwill and prepares an approved list of them. The buyers
of the company approach the factoring agency for discounting their purchases
receivables drawn in favor of company by seller. Then the factor discounts the
bill without recourse and makes the payment to the seller.
§ Disclosed and Undisclosed Factoring
In disclosed factoring
the name of the factoring agency is mentioned in the invoice by the supplier
asking the buyer to make payment to factor on the due date. However supplier
can bear the risk of bad debts without passing to factor.
In the undisclosed factoring the
name of the factor is not mentioned yet the control lies with the factor.
Comments
Post a Comment